Amazon EKS manages the Kubernetes control plane

In a standard Kubernetes deployment, you are responsible for designing, implementing, and maintaining all components of the control plane and the worker nodes.
Amazon EKS provides a scalable, highly available control plane. Amazon EKS automatically manages the availability and scalability of the Kubernetes API servers and the etcd persistence layer for each cluster.
This gives you more time to focus on running your application workloads in Kubernetes.
Amazon EKS availability and API
The Amazon EKS control plane consists of at least two API server nodes and three etcd nodes across three Availability Zones. Amazon EKS automatically detects and replaces unhealthy control plane nodes, which removes a significant operational burden for running Kubernetes. With this capability, you can focus on building your applications instead of managing AWS infrastructure.
To get started with Amazon EKS, you provision your cluster of worker nodes. Amazon EKS handles the provisioning, scaling, and management of the Kubernetes control plane in a highly available and secure configuration. You then connect to the Amazon EKS cluster using the graphical or command line interface. After you’ve connected to the Amazon EKS cluster, you’re ready to deploy your Kubernetes applications to your Amazon EKS cluster. You can do this the same way that you would with any other Kubernetes environment.
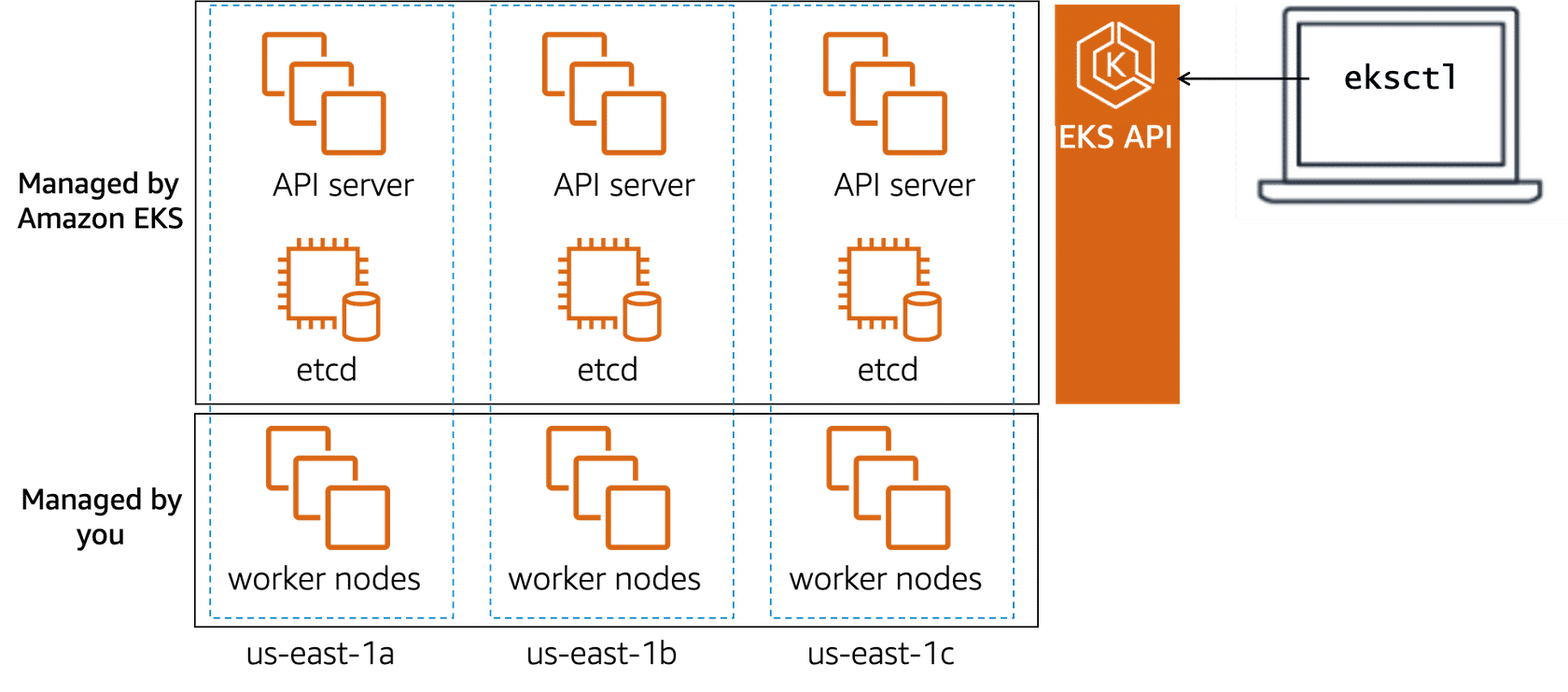
Amazon EKS manages the Kubernetes control plane with the Amazon EKS API. You can use one of two CLIs to interact with the Amazon EKS API: Amazon EKS CLI or eksctl. With the eksctl command line utility, developed by Weaveworks, you can create and manage Kubernetes clusters on Amazon EKS. The eksctl utility uses AWS CloudFormation in the background to build clusters based on the options you specify. You will learn the details of how to provision a cluster later in this course.
Review: Whose API am I using?
Working with two separate APIs and their respective tools adds complexity to managing your environment when getting started with Amazon EKS. Asking yourself the question, “Is this object directly controlled by Amazon EKS?” simplifies the next step to take. If the answer is yes, then use the Amazon EKS API to manage that object. For all other objects, use the Kubernetes API.
Select each of the following two tabs for detailed examples.
You use the Amazon EKS API for anything that Amazon EKS manages. As you have learned, this includes the entire control plane (creating and managing the cluster). In later modules, you learn how Amazon EKS can also manage parts of the data plane using features such as managed node groups and AWS Fargate.
Review the table for example tasks.
Note: Screen readers should enter table mode to read the following table.
| Task | Sample Command |
|---|---|
| Create a cluster. | eksctl create cluster |
| Delete a managed node group. | eksctl delete nodegroup –cluster=${clusterName} –name=${nodegroupName} |
| Get the Fargate profile of the cluster. | eksctl get fargateprofile –cluster ${clusterName} |
Visit the official eksctl website for more examples.
Use the Kubernetes API for managing Kubernetes objects such as pods, deployments, and namespaces.
Review the table for example tasks.
Note: Screen readers should enter table mode to read the following table.
| Task | Command Example |
| Get a list of pods in the default namespace. | kubectl get pods |
| Get a list of namespaces. | kubectl get namespaces |
| Create a deployment in the default namespace. | kubectl apply -f nginx-deploy.yaml |
Visit the Kubectl Reference Docs for more examples.
